Pipeline
You can scroll left and right to view the full content.
| Pipeline | Development Projects | Target diseases | Development of drug candidate | Safety test | Preclinical trials | Clinical trial - phase 1 | Clinical trial - phase 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FT005 | FT005-002 (Hulk) | Chronic kidney disease |
|
||||
| Sarcopenia (muscle atrophy with aging) |
|
||||||
| Muscular dystrophy |
|
||||||
| FT006 | FT006-001 (Batman) | COVID prevention |
|
||||
| FT007 | FT005-002 (Hulk) | Cancer cachexia |
|
||||
| FT005-007 (Steve) |
|
||||||
| FT009 | FT005-002 (Hulk) | Type 2 diabetes |
|
||||
| FT011 | FT005-005 (Paul) | Melanoma (skin cancer) |
|
||||
| FT012 | FT005-004 (Kyte) | Melanoma (skin cancer) |
|
FT005-002 (Hulk) Project (Target antigen: GDF-8, myostain)
Future & Tech leverages its proprietary GOST technology to develop immune therapeutics that induce muscle growth. Myostatin, a protein that inhibits muscle growth, is known to be expressed in all vertebrate muscle cells, including humans. Therefore, myostatin and its receptor is the most researched target proteins for developing muscle disorder therapies among most global pharmaceutical companies. Future & Tech continues to develop myostatin-targeting therapeutics aiming to promote muscle generation and prevent muscle loss, including the treatments for chronic kidney disease, sarcopenia, muscular dystrophy, type 2 diabetes, and cancer cachexia.
Research by global pharmaceutical companies related to myostatin and activin receptor targets
Myostatin signaling pathway and muscle loss
(1)SP : Signal Peptide
(2)LAP : Latency-associated peptide
The precursor myostatin protein consists of the N-terminal (NH2) signal peptide (SP) for extracellular secretion, and the C-terminal (COOH) that contains nine conserved cysteine resideus (Cys) involved in homodimerization. The activation of the myostatin precursor occurs in the Golgi apparatus, where it is cleaved at the RSRR/ site by furin, a serine protease, that separates the precusor into the latency-associated peptide (LAP) and the mature myostatin.
Mature myostatin is secreted into the circulatory system to be relocated to the muscles. Myostatin binds to activin type IIB or type IIA (ActRIIB/A) receptors on muscle membranes to cause dimerization. This activates type I activin receptor serine kinases (ALK4, ALK5, or ALK7) by phosphorylation, starting the signal pathway. This in turn, phosphorylates Sma- and Mad- related proteins, SMAD2 and SMAD3, which form a complex with SMAD4. The complex then translocates into the nucleus, leading to changes in gene transcription. In addition, myostatin suppresses phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase(PI3K) and Akt activity, reducing phosphorylation of the forkhead box precurosr factor (FoxO). Dephosphorylated FoxO enters the cell nucleus and activates transcription of the muscle RING-finger protein-1(MuRF1) and atrogin-1, which leads to muscle protein degradation via ubiquitination, proteasome, or autophagy. Myostatin also activates the integrated(WNT)/β-catenin pathway and the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) that regulate the transcription of atrophy-related genes. In the longer time horizon, myostatin’s effects are most evident in skeletal muscles, heart, and liver, with recent discoveries suggesting direct impact on adipose tissues and blood vessels.
- Chronic kidney disease is a condition in which the kidney’s function continues to decline and becomes unrecoverable, blocking the kidney from effectively filter metabolic waste from the blood. As shown in the below figure, this leads to increased resistance to insulin, imbalances in hormones, increased inflammation, increased urine acidity, along with elevated concentration levels of myostatin in the bloodstream.
(1) CKD: Chronic Kidney Disease
- CKD increases insulin resistance, metabolic acidosis, inflammation, and hormal imbalance, requiring hemodialysis. CKD leads to increased protein degradation, decreased protein synthesis, and reduced muscle regeneration that ultimately result in muscle loss.
- FT005-002 is under development as a candidate treatment to induce kidney function recovery, which neutralizes myostatin associated with CKD to prevent muscle loss and induce formation of skeletal muscle.
(1)eNOS : endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase
(2)NO : Nitric
Oxide
(3)UPS : Ubiquitin-proteasome system
Muscle wasting and kidney disease regulation are interconnected through muscle-kidney cross-talks.
· Myostatin and chronic kidney disease (CKD)
- One of the major complications of CKD is muscle loss that is accompanied by protein-energy wasting. Increasing myostatin levels inhibit muscle protein synthesis while accelerating muscle breakdown, leading to muscle loss.
- CKD is characterized by chronic inflammation, where myostatin expression may further accelerate the condition. Increased inflammation leads to faster muscle loss, where the production of myostatin protein serves as a key mediator of muscle degradation in CKD.
- Myostatin has been consistently and repeated proposed as a potential biomarker for muscle loss in CKD. Elevated myostatin levels show correlation with the severity of muscle wasting, which can provide insights into the patient’s metabolic and nutritional status.
- Due to myostatin’s role in muscle loss in CKD, many global pharmaceutical companies are actively engaged in the research of myostatin as a therapeutic target protein for CKD. Inhibiting or neutralizing the expression of myostatin may help to preserve muscle mass and improve the health of CKD patients.
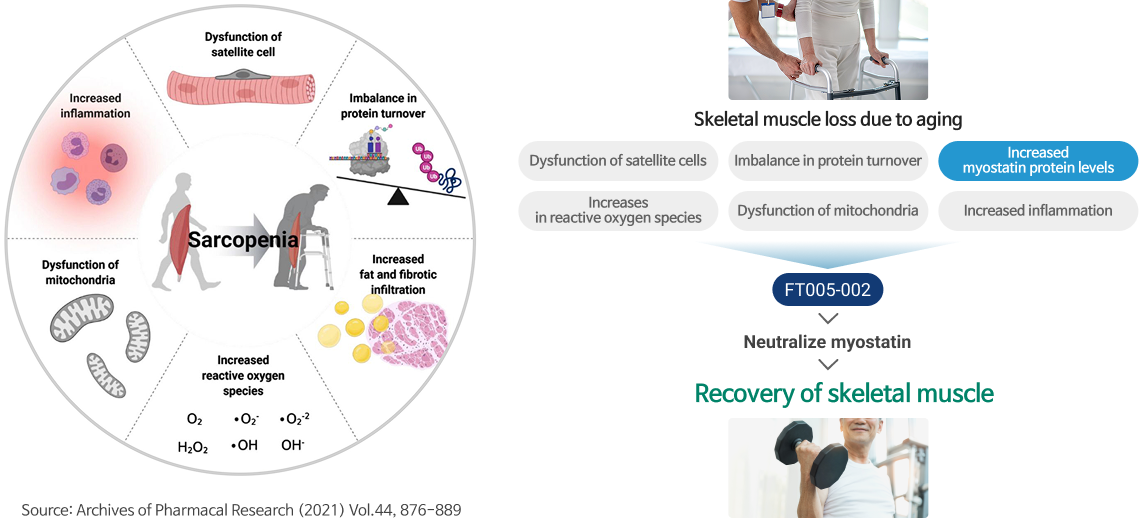
Causes of sarcopenia
- Myostatin levels naturally increase in the bloodstrem as people age, leadin gto skeletal muscle loss.
- Also, increased inflammation, reactive oxygen species, and dysfunction of mitochonria accelerate muscle cell degradation and therefore aging.
- FT005-002 neutralizes myostatin in the bloodstream, induces skeletal muscle growth, and delays aging.
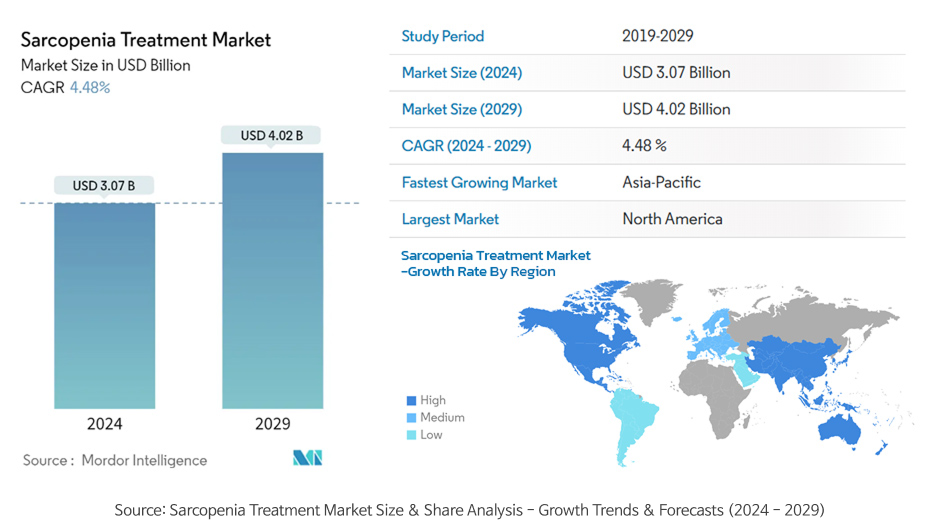
Sarcopenia treatment market size
- The sarcopenia treatment market is estimated at USD 3.07 billion as of 2024, which is expected to grow to USD 4.02 billion by 2029.
Technology transfer plan for sarcopenia immunotherapy
| Prospective technology recipient | Target milestone | Total technology transfer target fee | Remarks (including terms of agreement) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Big Pharma | Phase 1 IND approval by 2029 | KRW 270 billion (5% of the market) | Royalty: 5% of revenue |
| Big Pharma | Phase 2 approval by 2031 | KRW 540 billion (10% of the market) | Royalty: 10% of revenue |
- Total sarcopenia market size (2031): USD 4 billion (approximately KRW 5.4 trillion. FX 1,350 KRW/USD)
- Muscular dystrophy is a genetic disorder caused by mutations in the dystrophin gene that leads to progressive muscle loss.
- While symptoms typically appear by age four, most patients do not survive beyond the age of 25.
Definitions of rare diseases by country
| Key metrics | US | Korea | Europe | Japan |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Established year | 1983 | 2000 | 2000 | 1993 |
| Number of patients | 200,000 or less | 20,000 or less | 250,000 or less | 50,000 or less |
| Incidence rate | 6 pts/10,000 | 4.25 pts/10,000 | 5 pts/10,000 | 4 pts/10,000 |
- In Korea, the term rare disease has been defined as a disease with 20,000 or less patients within the country or an incidence rate of 4.25 per a population of 10,000.
Muscular dystrophy immunotherapy
| Mode of action |
|
|---|---|
| Development progress |
|
| Market size |
|
| Competitors and their products |
|
Technology transfer plan for muscular dystrophy immunotherapy
| Prospective technology recipient | Target milestone | Total technology transfer target fee | Remarks (including terms of agreement) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Big Pharma | Phase 1 IND approval | KRW 3.65 billion (5% of the market) | Royalty: 5% of revenue |
| Big Pharma | Phase 2 approval | KRW 730 billion (10% of the market) | Royalty: 10% of revenue |
Cookie notice
By clicking 'Accept all cookies', you agree to the storing of cookies on your device and to the associated processing of data to enhance site navigation, analyse site usage, and assist in our marketing and performance efforts.
Cookie Consent Settings
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
- Functional Cookies
- Marketing/Advertising Cookies
- Statistics Cookies